Tech Security Essentials are more than a checklist—they are a practical, ongoing discipline for protecting information in our hyperconnected world. In today’s digital era, every device and service is interconnected, making strong defenses essential for individuals and organizations alike. This introductory framework helps reduce risk, safeguard data, and keep operations resilient as networks span devices, clouds, and endpoints. By focusing on data protection, cybersecurity best practices, and data privacy, this approach also supports secure remote work and strong device security. In short, embracing these fundamentals translates into practical steps that organizations and individuals can start today.
Viewed through the lens of information security basics, these essentials act as guardrails for protecting data across devices, networks, and cloud services. In other words, this framework translates technical controls into everyday practices that improve cyber hygiene, reduce risk, and preserve privacy. The aim is to build resilience by combining strong authentication, careful data handling, and mindful device management. By aligning with concepts such as data protection, privacy by design, and secure access, organizations can implement practical measures without stifling productivity.
Tech Security Essentials: A Practical Framework for Data Protection and Cybersecurity Best Practices
Tech Security Essentials integrates data protection with cybersecurity best practices to form a practical, repeatable baseline. Start by building a data inventory—know what personal data you have, where it resides, and how sensitive it is—so you can apply least-privilege access and data minimization, enabling safer data processing and reducing exposure across endpoints, apps, and cloud services. Encryption should be established for data at rest and in transit, tied to a robust key management program, ensuring that even if a breach occurs, information remains unreadable.
Then, define defense-in-depth with secure configuration, patch management, MFA, phishing awareness, and regular access reviews to sustain data protection and cybersecurity best practices. Privacy-by-design should be baked into systems: offer clear notices, minimize data collection, and implement data retention and deletion controls to uphold data privacy while maintaining operational resilience. In short, Tech Security Essentials turn broad security goals into actionable routines that protect data integrity and availability without impeding productivity.
Tech Security Essentials for Secure Remote Work and Device Security in a Hyperconnected World
Secure remote work begins with secure access to corporate resources, through ZTNA or VPNs, plus continuous authentication and context-aware controls. Enroll endpoints in device management, deliver timely security updates, and apply privacy-conscious collaboration settings to protect data privacy while enabling distributed teamwork. DLP policies and restricted sharing help prevent leakage, while ongoing training reinforces cybersecurity best practices even for remote staff. This approach aligns with data protection and secure remote work goals.
Device security remains the frontline. Establish baseline configurations, enforce encryption, secure boot, and tamper-evident recovery. Regularly audit installed apps and permissions, disable unnecessary services, and maintain a lean software footprint to minimize attack surfaces. Integrate identity and access management (IAM) with adaptive authentication and RBAC, monitor for anomalous access, and rehearse incident response to ensure rapid containment and recovery under a hyperconnected threat landscape. By treating Tech Security Essentials as an ongoing discipline, organizations can maintain data protection, data privacy, and device security across all endpoints.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Tech Security Essentials and how do they support data protection and data privacy in a modern organization?
Tech Security Essentials are an ongoing, practical framework of foundational controls that protect information across devices, networks, and clouds. They integrate data protection (data inventory, least-privilege access, encryption, key management), cybersecurity best practices (secure configuration, patch management, MFA, phishing awareness), and data privacy (privacy-by-design, data minimization, retention controls). By implementing these elements together, organizations reduce exposure and improve resilience. Practical steps: map data and classify sensitivity; enforce least-privilege access and robust IAM; encrypt data at rest and in transit with a solid key-management plan; adopt secure remote work practices; train users to recognize phishing; and continuously monitor and update security configurations.
How can organizations implement Tech Security Essentials to enable secure remote work and strengthen device security?
To implement Tech Security Essentials for secure remote work and device security, start with secure access to resources (VPN or zero-trust with continuous authentication); enroll endpoints in device management and enforce baseline configurations; keep operating systems and applications up to date; enable encryption, secure boot, and privacy-conscious collaboration with data loss prevention. Strengthen cybersecurity best practices with MFA and strong credential hygiene, and align data protection and data privacy controls (data minimization, retention, data sharing policies). Finally, maintain incident response planning, regular backups, and monitoring to detect and respond to threats quickly.
| Topic | Key Points | Practical Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Data Protection Foundation | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability; data inventory and classification; least-privilege access; data minimization. | Create a data inventory; classify data by sensitivity; apply least-privilege access; collect only what you need; store securely; retain data only as long as necessary. |
| Encryption | Foundational: protects data at rest and in transit; use strong, standardized encryption; robust key management; regular access auditing. | Implement strong encryption; establish a robust key management process; regularly audit access controls and monitor for anomalies. |
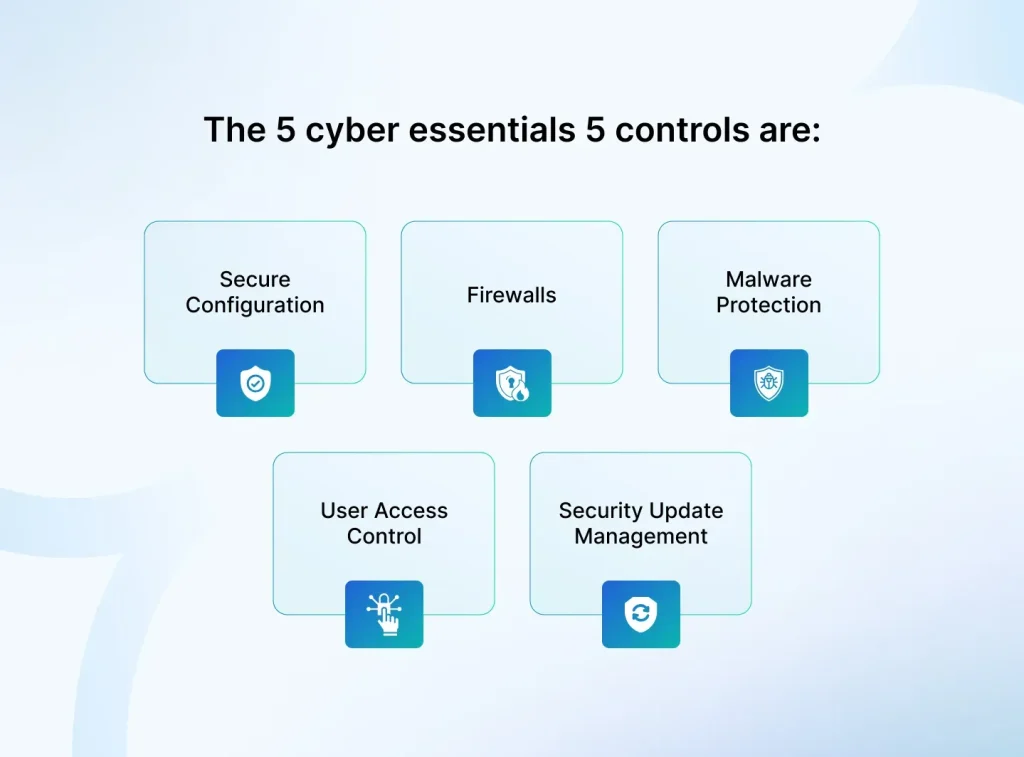
| Cybersecurity Best Practices | Defense in depth; secure configuration; patch management; MFA; phishing awareness. | Harden devices/services/apps; enable automatic updates; apply patches promptly; implement MFA; train users on phishing and social engineering. |
| Data Privacy by Design | Privacy embedded in design; transparency; data minimization; anonymization; retention; data subject rights. | Incorporate privacy-by-design from the start; provide clear notices; minimize data collection; implement retention and deletion controls; support data subject rights. |
| Secure Remote Work | Secure access (VPN/ZTNA); continuous authentication; device management; privacy-conscious collaboration; DLP. | Provide secure access to resources; enroll endpoints; keep security updates current; configure privacy-friendly collaboration; implement DLP. |
| Device Security | Baseline configurations; keep OS/apps updated; disable legacy services; disk encryption; secure boot; tamper-evident recovery; review app permissions. | Enforce baseline security configurations; keep software up to date; disable unnecessary features; enable disk encryption and secure boot; minimize installed apps; review app permissions regularly. |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Centralized identity; adaptive authentication; least privilege; monitoring; remediation; living program. | Use centralized IAM; implement RBAC and MFA; apply adaptive authentication; monitor for anomalies; automate remediation; update as roles/devices evolve. |
| Incident Response and Resilience | Well-defined incident response plan; roles; communication; tabletop exercises; backups; recovery objectives; rapid detection and coordinated response. | Define IR plan; assign roles and communication protocols; conduct tabletop exercises; maintain backups and tested restore procedures; align recovery objectives with business needs. |
| Practical Real-World Steps | Concrete steps you can take today. | – Map your data: inventory, classify, least-privilege; – Encrypt and back up: at rest/in transit; offline/immutable copies; – Strengthen authentication: MFA, passphrases, password managers; – Patch promptly: ongoing cadence; automatic updates; – Train continuously: security awareness; – Secure remote work: secure access, device management, privacy-conscious collaboration; – Harden devices: baseline configs, encryption, secure boot, minimize apps; – Monitor and respond: logs, alerts, IR plan. |
| Why These Steps Matter in a Hyperconnected World | Hyperconnected environments multiply opportunities and risks; Tech Security Essentials provide a flexible, adapt-to-context framework that can be tailored to risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and business models. | Tailor the Essentials to your risk profile, regulatory landscape, and organizational needs. |
| Measuring Success and Maintaining Momentum | Success is multidimensional: fewer incidents, faster recovery, higher security process satisfaction, and stronger compliance. | Regular risk assessments; policy reviews; adapt controls in response to threat intelligence and changing technology landscapes. |
Summary
Conclusion: Tech Security Essentials provide a practical, scalable path to safeguarding data and maintaining trust in today’s hyperconnected world. By focusing on data protection, cybersecurity best practices, data privacy, secure remote work, and device security, organizations build resilience and a safer digital life. The journey is ongoing, but each deliberate action grounded in Tech Security Essentials strengthens defenses against evolving threats and supports a secure, trusted technology environment.