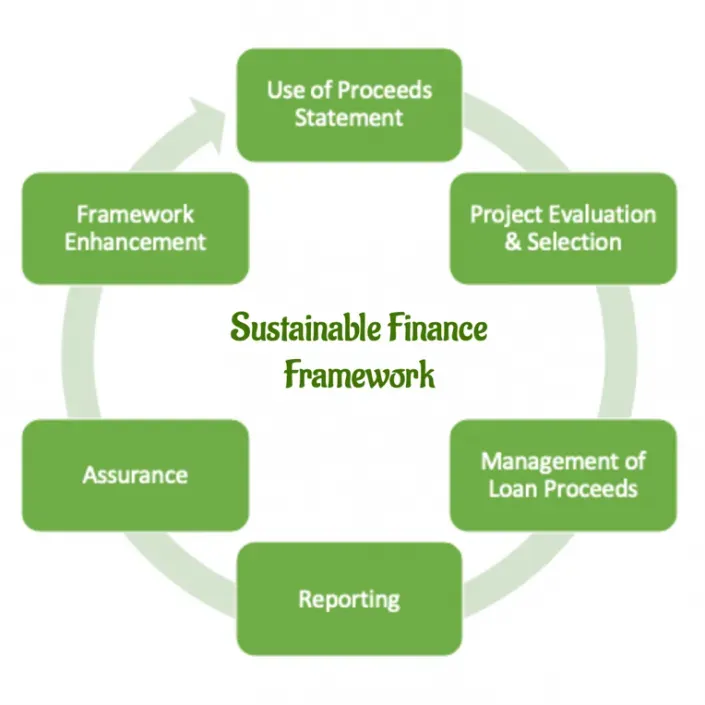
Sustainable Finance reshapes how individuals and institutions allocate capital with ambition and accountability. By blending financial goals with environmental stewardship and social responsibility, it brings concepts like impact investing, ESG investing, and socially responsible investing into mainstream portfolios. Investors increasingly demand measurable outcomes, such as reduced carbon emissions or improved governance, while pursuing attractive risk-adjusted returns under sustainable investing strategies. From green finance initiatives to broader social impact, this approach aligns value creation with value for people and the planet. As institutions modernize portfolios, sustainable finance becomes a practical framework for resilience, transparency, and long-term growth.
Beyond the formal label, this approach embraces responsible investing, ethical finance, and climate-aware capital allocation. It is often analyzed through related concepts and LSI-friendly terms such as governance quality, stakeholder value, and climate risk management. The core idea is to couple financial viability with positive social and environmental outcomes, using metrics, transparency, and impact measurement. Practitioners seek climate-resilient opportunities, inclusive growth, and accountable governance to guide portfolio construction. Together, these terms reflect a shared objective: align capital with durable progress that benefits people, the planet, and long-term performance.
Sustainable Finance in Practice: Integrating ESG Investing and Impact Metrics
Sustainable finance translates the ideas of responsible capitalism into concrete investment choices. It blends environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance with traditional risk-reward analysis, elevating ESG investing and impact investing to core planning principles. Investors assess not only price and return but also how a portfolio affects carbon footprints, community outcomes, and corporate stewardship. By adopting sustainable investing strategies, they can balance risk, resilience, and long-term growth while aligning capital with values. Standardized metrics, such as IRIS+ and SASB, help quantify social and environmental impact alongside financial performance.
This approach expands the toolkit with green finance instruments like green bonds and sustainable loans, and it emphasizes ongoing engagement with issuers. Through ESG integration, positive and negative screening, and thematic and impact investing, portfolios can be structured to reduce climate risk, support energy efficiency, water stewardship, and inclusive growth. The bottom line is that sustainable finance aims to deliver durable value by managing material sustainability factors that drive long-term profitability and societal benefit.
Impact Investing and Green Finance: Building Resilient Portfolios with Socially Responsible Investing
Impact investing and green finance channel capital toward projects that generate measurable social and environmental benefits while aiming for competitive returns. In renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and clean transportation, these strategies seek to create jobs, reduce emissions, and foster equitable access to essential services. Socially responsible investing guides capital toward governance-focused firms and inclusive business models, reinforcing resilience across economic cycles while delivering visible impact alongside returns.
Investors leveraging these approaches use green bonds, social bonds, and blended finance to structure risk-adjusted opportunities. The goal is to pair impact outcomes—carbon reduction, community benefits, and access to services—with sustainable investing strategies that manage volatility and align with fiduciary duties. Through rigorous impact measurement, transparent reporting, and active stewardship, portfolios can achieve durable performance that respects both people and the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does sustainable finance integrate ESG investing to balance financial returns with environmental and social outcomes?
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment analysis, expanding beyond traditional risk–return models. Through practices like ESG investing, impact investing, and green finance, investors consider profit alongside environmental and social impacts. This approach helps manage climate risk, governance quality, and equity considerations while pursuing attractive risk‑adjusted returns. Metrics such as carbon footprint, job creation, and access to essential services support transparent reporting and performance assessment.
What practical strategies in impact investing and sustainable investing strategies can help deliver both returns and measurable impact?
Key strategies include ESG integration to embed sustainability data in financial analysis; Positive and Negative Screening to favor sustainable leaders and avoid misaligned activities; Thematic and Impact Investing to target sectors with clear sustainability benefits; Engagement and Stewardship to influence governance and performance; and Green and Sustainable Finance instruments like green bonds and sustainable loans. Impact is measured using frameworks such as IRIS+ and SASB, plus carbon and social indicators, enabling credible reporting. Together these approaches seek durable risk-adjusted returns while delivering tangible environmental or social outcomes.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Sustainable Finance? | Integrates ESG criteria into investment analysis and decision-making, expands beyond traditional risk-reward, and uses modes such as ESG investing, impact investing, green finance, and sustainable investing strategies to channel capital toward lower carbon emissions, equitable outcomes, and responsible governance. |
| Investing with Impact and Profit: Core Idea | Balances measurable impact outcomes with financial returns; not charity. The best sustainable investments balance both—delivering attractive risk-adjusted returns while achieving explicit social or environmental goals, using both financial metrics and impact metrics (e.g., carbon reduction, community benefits). |
| Strategies for Implementing Sustainable Finance | Clear objectives; strategies include ESG Integration, Positive and Negative Screening, Thematic and Impact Investing, Engagement and Stewardship, Green and Sustainable Finance Instruments. |
| Measuring Impact and Performance | Rely on frameworks like IRIS+ and SASB; use carbon footprint and intensity metrics; monitor social indicators such as job creation or education access; aim to link investment thesis to measurable outcomes; transparent reporting, third-party verification, and independent assessments reduce greenwashing. |
| Risk Considerations and Market Realities | Benefits include diversification and resilience; risks include data quality, trade-offs, greenwashing, and evolving regulation. |
| Tailoring to Different Investors | Not one-size-fits-all; individuals, family offices, pension funds, and endowments have different constraints and horizons; priorities vary, but the core principle remains to align investments with values while preserving financial integrity. |
| Case Studies and Real-World Examples | Renewable energy projects reduce carbon, create jobs, and provide steady cash flows; investments in healthcare access improve outcomes; strong governance and transparent reporting support ongoing improvement; impact and profitability are not mutually exclusive. |
| Practical Roadmap for Investors | Define impact and return objectives clearly; build a diversified mix across asset classes; use ESG integration for security selection and risk management; implement thematic and impact-focused strategies; robust measurement and reporting; engage with companies through shareholder rights and dialogue. |
| The Role of Policy and Market Trends | Policy developments and market trends shape sustainable finance; climate-related disclosure requirements, green incentives, and evolving governance standards; standardized metrics and better data reduce information asymmetry and enable efficient capital allocation toward sustainable strategies and green finance initiatives. |
Summary
Sustainable Finance represents a holistic approach to allocating capital that blends financial objectives with environmental stewardship and social responsibility. By integrating ESG criteria into investment analysis, embracing impact and green finance, and applying rigorous measurement and governance practices, it seeks to align profits with durable, positive outcomes. As climate risk, resource scarcity, and social inequality challenge markets, investors increasingly pursue strategies that deliver both value and value-driven impact. A practical roadmap—defining clear objectives, diversifying across asset classes, and maintaining transparent measurement and reporting—helps ensure that Sustainable Finance portfolios achieve resilient performance while advancing climate action, social equity, and responsible governance.