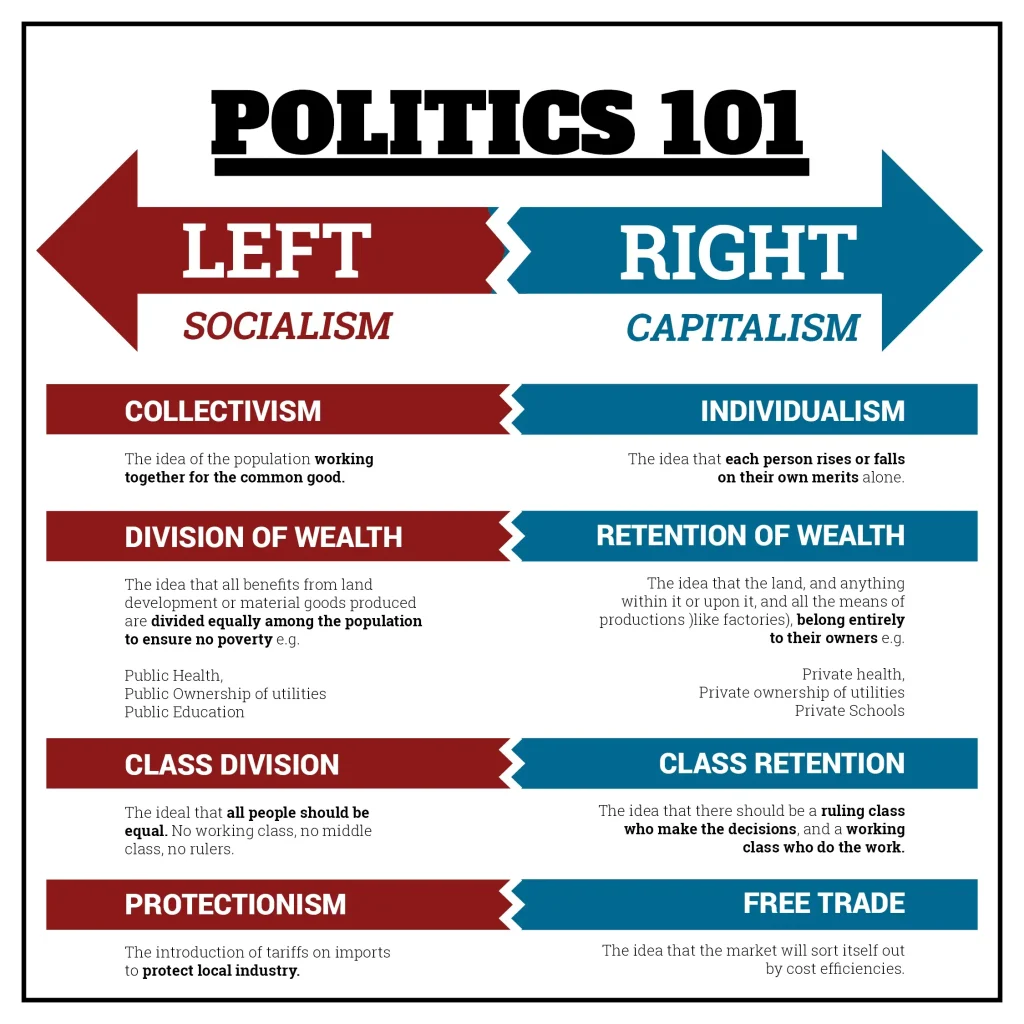
Politics explained can feel overwhelming, especially in a media landscape overflowing with opinions. This concise guide cuts through the noise to highlight the big ideas voters need to participate thoughtfully and responsibly in a complex political landscape. To start, democracy basics show how power rests with people, how elections shape who governs, and how rights fit with responsibilities. By breaking down the mechanics of voting, representation, and accountability into clear steps, you can see what each part does. With practical takeaways you can apply on Election Day, this primer helps you evaluate claims, participate more effectively in democracy, and bring constructive questions to conversations with neighbors and policymakers.
Viewed through a different lens, this topic becomes the study of how societies organize power and guide collective decisions. Think in terms of public governance, electoral frameworks, and the way constitutional design shapes everyday life. Comparing federal versus unitary models, presidential versus parliamentary arrangements, and how courts interact with legislatures reveals how policies emerge. This LSI-inspired framing helps readers connect ideas across news coverage, civic discussions, and policy debates, highlighting related threads like governance structures, citizen participation, and policy outcomes.
Politics explained: democracy basics, how elections work, and voting rights
Democracy basics: At its core, democracy is a system where power rests with the people. Citizens have a say in decisions that affect their lives, and that authority is constrained by the rule of law. Three ingredients—meaningful participation, fair competition, and protection of rights—keep democracy healthy. Meaningful participation means eligible voters can engage in public discussions, join civic life, and hold leaders accountable. Fair competition requires free and open elections and a level playing field for candidates and parties. Rights protection safeguards minority voices and ensures basic liberties even when majorities make policy.
How elections work: The mechanics vary by country and even within regions, but the essential idea is to translate preferences into representation. In simple plurality systems, the candidate with the most votes wins, which can produce clear mandates but leave many voters unrepresented. In proportional systems, seats align with share of votes, fostering multi-party coalitions and more diverse representation, though sometimes at the cost of faster decision-making. Turnout and accessibility matter as much as platforms; barriers like registration rules, polling hours, and identification requirements shape who gets to participate.
Voting rights: Access and responsibility in practice. Voting rights are more than a legal checkbox; they determine who can influence public policy. Access to polling places, up-to-date registration, and clear instructions on voting options—such as in-person, early voting, or mail-in ballots—shape real-world participation. Civic engagement goes beyond casting a ballot, including following issues, contacting representatives, and volunteering. When voters understand their rights and how to exercise them, elections become meaningful instruments for governance.
Checks and balances: how power is restrained and political systems explained
Checks and balances: In most democracies, power is divided among legislative, executive, and judicial branches to prevent overreach. Each branch has distinct roles and independent powers, with tools like vetoes, confirmations, and judicial review serving as brakes or accelerators as needed. When checks function well, they reduce the risk of rash policymaking and protect rights even when political winds shift. For voters, understanding these constraints helps separate ambitious promises from feasible reforms.
Political systems explained: Beyond courts and parliaments, the structure of the state shapes governance. Federal systems distribute sovereignty across levels, allowing responsiveness to local needs but creating complexity; unitary systems centralize power, enabling swift action but risking one-size-fits-all policies. Presidential versus parliamentary models offer different dynamics: fixed executive terms vs fusion of powers and responsive coalitions. Recognizing these patterns—the political systems explained—helps voters assess reforms and anticipate policy paths.
Practical implications for voters: When evaluating candidates and proposals, consider how the system constrains power, how coalitions form, and what that means for accountability and stability. Look for evidence of how budgets pass, how courts interpret laws, and how independent media and civil society can monitor action. A knowledgeable voter uses checks and balances as a lens to ask tough questions about feasibility, timelines, and trade-offs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Politics explained: what are democracy basics and why do they matter for voters?
Democracy basics mean that power is held by the people and include three core ingredients: meaningful participation, fair competition, and rights protection. For voters, these ideas help you recognize when institutions are healthy, how elections reflect public will, and when reforms are needed. Practical takeaway: stay informed, verify claims from credible sources, and participate in community dialogue to strengthen accountability.
Politics explained: how elections work and what voting rights mean in practice?
Elections translate citizen preferences into representation and policy, through systems such as plurality or proportional representation that shape outcomes and coalitions. Voting rights cover access to polling places, accurate registration, and clear procedures. Know deadlines, allowed voting methods, and required documentation. Practical steps: follow official election sources, check your registration, and vote through the method available in your area.
| Topic | Core Idea | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Democracy basics | Power rests with the people; three ingredients: meaningful participation, fair competition, protection of rights. | Elections are a primary mechanism; healthy democracy also relies on transparent institutions, independent courts, a free press, and active civil society; recognize when reforms strengthen accountability and participation. |
| How elections work | Different electoral systems (plurality vs proportional representation); turnout and accessibility matter. | Know how ballots are counted, what system is in place, and how it shapes representation and policy outcomes; understand registration and voting options. |
| Voting rights | Access, participation, and responsibility; the practical ability to influence public policy. | Civic engagement goes beyond voting; informed participation strengthens legitimacy and trust in elections. |
| Checks and balances | Power is divided among legislative, executive, and judicial branches with tools to limit others’ actions. | Prevents overreach, protects rights, and provides a framework to evaluate political promises and policy feasibility. |
| Political systems explained | Federal vs unitary structures; presidential vs parliamentary models; regimes blend features. | Systems shape accountability, representation, and stability; understanding reforms helps voters compare options and anticipate policy paths. |
| Policy, politics, and the everyday voter | Policy = concrete plans for laws, spending, and regulations; Politics = the arena where these proposals compete. | Look for substance, evidence, financing, and implementation; distinguish policy details from campaign messaging to evaluate proposals effectively. |
| Critical thinking and information literacy | Verify claims with credible sources; compare multiple outlets; distinguish opinion from verified facts. | Adopt a habit of thoughtful scrutiny to improve decisions and contribute to healthier public dialogue. |
| Practical steps for voters | Local rules: registration deadlines, polling locations, available voting methods; follow official sources; attend forums; discuss issues respectfully; participate in community groups. | These steps translate knowledge into action, strengthening democratic participation and ensuring informed choices on Election Day. |
Summary
Politics explained shows how democracy relies on informed participation, robust institutions, and ongoing dialogue among citizens. By understanding democracy basics, how elections work, voting rights, checks and balances, and the different political systems that shape governance, you gain a clearer lens for evaluating proposals and recognizing what advances or undermines the common good. The goal isn’t to master every nuance of every debate but to cultivate the habits of rigor, curiosity, and civic responsibility that empower you to contribute meaningfully to your community. When you combine critical thinking with active engagement—learning, asking questions, voting, and speaking up—you participate in democracy as a practical, empowering practice rather than a distant ideal. That is the essence of Politics explained: turning complex ideas into everyday actions that improve governance and, ultimately, everyday life.