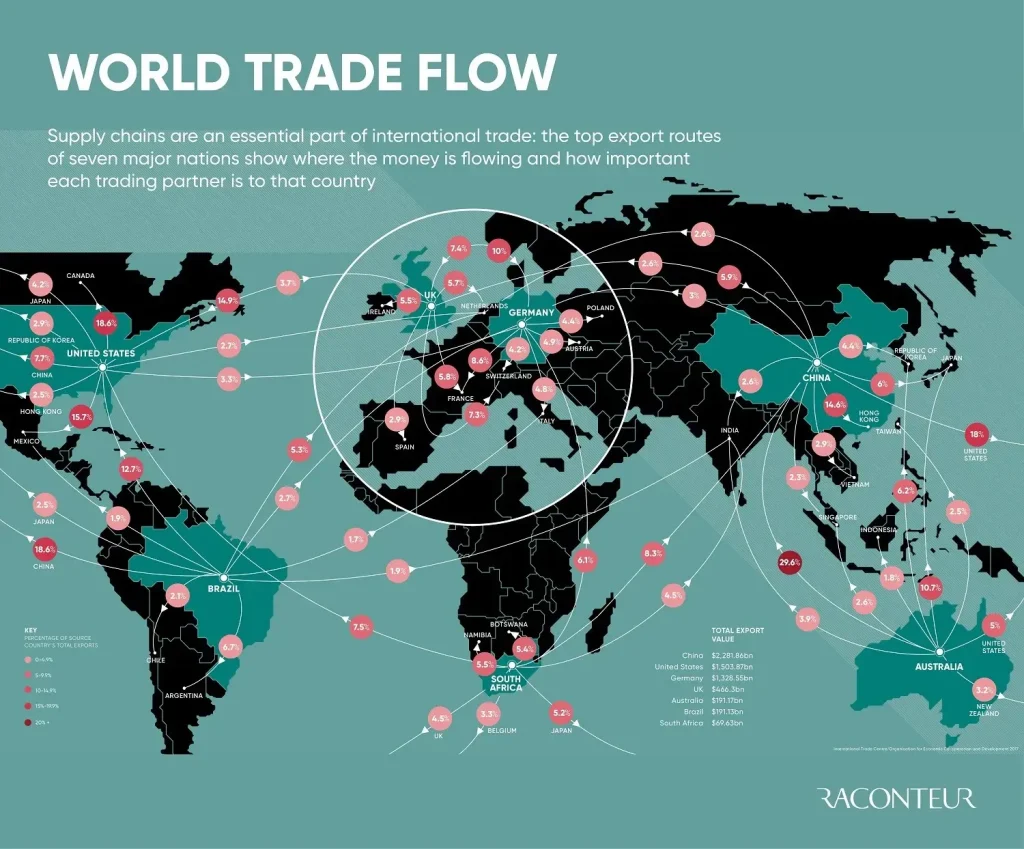
Global trade sits at the center of today’s business landscape, shaping how companies source, manufacture, and distribute goods across borders. Tariffs impact on global trade by altering prices, shifting sourcing strategies, and reshaping where firms locate manufacturing. In global supply chains, firms invest in resilience, diversify suppliers, and improve digital visibility to weather shocks. The post-pandemic recovery adds momentum to reforms in international trade policy and to investments in trade facilitation. A growing emphasis on supply chain resilience and smarter risk management will determine which firms thrive as global trade evolves.
Viewed through alternative terms, the topic expands to global commerce, cross-border exchange, and the health of interconnected trade networks that span continents. Shifts in policy signals, tariff regimes, and customs procedures influence market access, supplier selection, and the speed of international business. LSI-inspired framing uses terms such as worldwide markets, international commerce policy, and cross-border logistics to capture related dynamics. By mapping these related concepts, companies can anticipate regulatory changes, adapt sourcing strategies, and build resilient networks that support sustained growth in an increasingly connected economy.
Global trade dynamics: Tariffs, policy shifts, and building supply chain resilience
Tariffs influence the cost structure of internationally sourced inputs and the prices that consumers see at the register. The tariffs impact on global trade is felt as higher input costs, altered competitiveness, and shifted investment incentives for manufacturers across borders. In the context of Global trade, tariff policy can reconfigure where goods are sourced, where factories are located, and how value chains are organized. To strengthen supply chain resilience, many firms are widening supplier diversity, investing in automation, and pursuing nearshoring to dampen tariff-related volatility and maintain steady production.
Companies are increasingly leveraging digital visibility and data-driven planning to anticipate tariff changes and supply disruptions. Multi-sourcing across regions, longer-term supplier contracts, and dynamic inventory buffering are becoming standard practices for those seeking to maintain service levels in a volatile policy environment. As part of building resilience in global supply chains, firms are also evaluating capital investment in regional hubs and flexible manufacturing capabilities to reduce exposure to cross-border shocks caused by tariff swings.
Post-pandemic recovery and international trade policy: shaping supply chain resilience
As economies recover from the health crisis, demand patterns are rebalancing and trade flows are gradually normalizing. The post-pandemic recovery is accompanied by a renewed emphasis on digital trade, paperless processes, and standardized cross-border protocols that reduce friction in global supply chains. Policymakers and firms alike are watching tariff schedules and international trade policy developments to anticipate opportunities in new markets and to mitigate risk from policy shifts that could stall momentum in Global trade activity.
Policy coordination plays a crucial role in sustaining growth. When trade agreements align with modernization of customs procedures and standards, it helps expand supply chain resilience and accelerate near-term recovery. For businesses, this means designing flexible sourcing strategies, investing in visibility technologies, and building regional networks that support faster, more reliable cross-border movement of goods—even as geopolitical tensions and tariff contexts evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the tariffs’ impact on global trade, and how does it shape global supply chains?
Tariffs raise import costs, affecting consumer prices and firm margins within global trade. They can shift sourcing toward domestic production or regional suppliers, altering the dynamics of global supply chains and trade flows. Over time, tariff policy may influence investment decisions, automation, nearshoring or reshoring, and the geography of production, impacting the efficiency and resilience of global trade networks.
How can businesses navigate international trade policy to support post-pandemic recovery and supply chain resilience?
Key strategies include diversifying sourcing, considering nearshoring where viable, and investing in digital trade tools that improve cross-border visibility. Strengthening end-to-end supply chain transparency and interoperable data standards supports post-pandemic recovery and builds supply chain resilience. Additionally, engaging with policymakers to pursue predictable tariff regimes, streamlined customs, and coordinated standards can accelerate growth in global trade.
| Topic / Section | Key Points | Implications for Global Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction |
| Sets context for how tariffs, resilience, and policy interact to affect opportunities and challenges in Global trade. |
| Tariffs and Global Trade |
| Tariff policy is a strategic variable that can alter the geography of production and the speed of goods moving through global value chains. |
| Global Supply Chains in a Post-Pandemic World |
| Creates a more adaptive, diversified network that can weather disruption while meeting customer demand in a timely way. |
| Post-Pandemic Recovery and Trade Growth |
| Recovery aided by digitalization and policy stability; tariffs help or hinder depending on predictability. |
| International Trade Policy and Business Strategy |
| Policy developments create opportunities and risk; proactive engagement with policymakers helps capitalize on favorable shifts. |
| Building Resilience Across Global Supply Chains |
| Results in a more robust and responsive Global trade network capable of withstanding shocks. |
| Practical Takeaways for Businesses and Policy Makers |
| Actionable guidance for stakeholders to navigate Global trade dynamics. |
Summary
Global trade is a dynamic landscape shaped by tariff policies, evolving supply chains, and the ongoing post-pandemic recovery. This descriptive overview highlights how tariffs influence costs and sourcing, why resilience and digital visibility are essential for modern global supply networks, and how coordinated policy can accelerate efficient cross-border commerce. For businesses, diversification, flexible logistics, and investment in digital infrastructure position them to navigate uncertainty and capitalize on opportunities in Global trade. As regions pursue nearshoring and regionalization, the geography of production may shift, but the overarching aim remains a more transparent, resilient, and efficient global trading system.