blockchain use cases beyond crypto are redefining how organizations think about data, trust, and collaboration across industries, moving beyond hype into durable capabilities that underpin processes, governance, and partner ecosystems, from healthcare to manufacturing, finance to energy, the trend is broadening the boundaries of what is considered auditable, compliant, and governance-ready. These evolving capabilities, anchored in decentralization, immutability, transparency, and programmable smart contracts, unlock efficiency, reduce latency in multi-party workflows, strengthen auditability, and automate complex operations—making blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency a practical and scalable business tool. Enterprise blockchain solutions are no longer fringe experiments but essential infrastructure that connects disparate systems and organizations with shared ledgers, near real-time visibility, and standardized data models, enabling faster onboarding of partners, automated reconciliations, and more resilient compliance. In blockchain in supply chain management, provenance tracking and tamper-evident records give brands confidence in authenticity, enable safer recalls, support ethical sourcing claims, and empower suppliers with transparent performance metrics across global networks. Beyond logistics, blockchain for data security and privacy shores up identity, access controls, consent management, and auditable trails, while blockchain applications in healthcare and finance demonstrate privacy-preserving data sharing, consent-driven data sharing, and compliant analytics across patient records, claims processing, and cross-border payments.
Viewed through the lens of distributed ledger technology and cross-organizational platforms, the same innovations take on different terminology yet share core value: secure, transparent, and automated data exchanges that reduce friction across partners. By emphasizing permissioned networks, digital identity, and verifiable credentials, this framing highlights how smart contracts and tamper-evident logs can streamline operations without exposing sensitive information. In practice, organizations are experimenting with interoperable data fabrics, governance models, and consent-driven access control to enable trusted collaboration across industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to finance and energy.
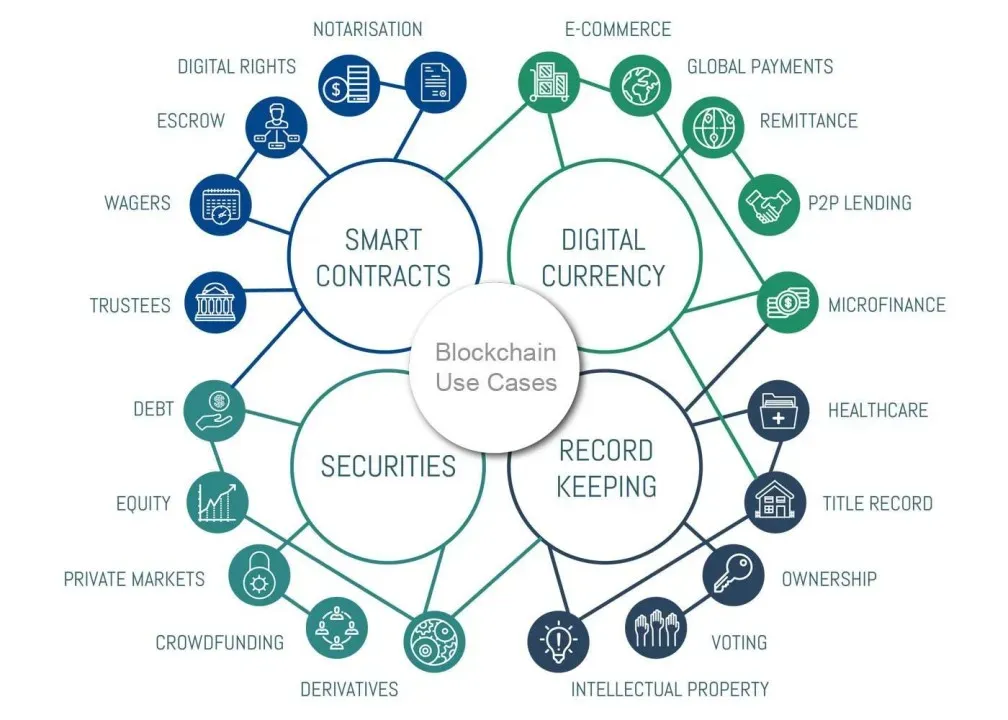
blockchain use cases beyond crypto: Real-world impact across industries
Blockchain’s core capabilities—decentralization, immutability, and programmable smart contracts—enable new ways to design processes and share trusted data across organizations. In practice, blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency are realized through solutions that connect people, systems, and data without a central gatekeeper. Enterprises are adopting enterprise blockchain solutions to replace paper-based workflows and siloed databases with near real-time visibility into transactions, provenance, and compliance events.
Examples span multiple sectors: blockchain in supply chain management tracks provenance from supplier to store, while blockchain for data security and privacy provides verifiable access controls and tamper-evident logs. Blockchain applications in healthcare and finance support secure record sharing, consent management, and auditable trails for regulatory compliance. These use cases illustrate how trust, transparency, and efficiency can be embedded into everyday operations without relying on crypto markets.
Implementing enterprise blockchain solutions: Best practices for successful adoption
To realize these benefits, organizations must design governance and architecture that scale. Enterprise blockchain solutions require clear data governance, cross-organizational consent, and interoperable interfaces with existing ERP and data platforms. Prioritizing privacy by design—using permissioned networks and selective visibility—helps address regulatory and risk concerns in areas like supply chain, healthcare, and finance.
Pilot projects should start small, with concrete ROI, defined success criteria, and a plan to scale. Build cross-functional teams that include IT, operations, legal, and compliance to validate workflows, smart contracts, and data-sharing agreements. This approach aligns with best practices for blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency and supports broader adoption of enterprise blockchain solutions, including ongoing improvements in blockchain in supply chain management and data security and privacy across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are enterprise blockchain solutions and how do they enable blockchain use cases beyond crypto?
Enterprise blockchain solutions refer to private or permissioned distributed ledgers that interoperate with existing systems to replace siloed processes with a shared, auditable source of truth. They support blockchain use cases beyond crypto by using smart contracts and interoperable ledgers to automate workflows, improve data integrity, and accelerate settlements. Benefits include faster cycle times, reduced reconciliation costs, stronger governance, and easier regulatory compliance for non-financial processes like procurement, manufacturing, and supplier collaboration.
How does blockchain in supply chain management improve provenance and efficiency beyond crypto?
Blockchain in supply chain management records immutable provenance data across suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers on a permissioned ledger, creating a transparent, auditable trail from source to sale. This enables traceability, rapid recalls, reduced fraud, and more accurate forecasting, while access controls protect sensitive information. It also supports blockchain for data security and privacy by providing tamper-evident audit trails and verifiable credentials for compliant data sharing. Smart contracts can automate payments and settlements, and the same approach underpins blockchain applications in healthcare and finance by enabling secure, verifiable data sharing.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What blockchain offers beyond crypto | Distributed ledger with immutability; single source of truth; smart contracts enable collaboration without a central intermediary; enables provenance, verifiable workflows, and controlled data sharing. |
| Enterprise blockchain solutions | Private/permissioned blockchains; interoperable, auditable layers; improves cycle times, reconciliation costs, and data accuracy outside crypto contexts. |
| Blockchain in supply chain management | Verifiable provenance and auditable trail; permissioned data visibility; supports tracing, authenticity, and recall effectiveness. |
| Data security and privacy | Self-sovereign identity (SSI) and DIDs; verifiable credentials; strong access control and tamper-evident audit logs for compliance. |
| Healthcare and finance applications | Secure patient data exchange with off-chain storage pointers; improved KYC/AML, faster cross-border payments, and transparent trade finance. |
| Other sectors | Energy trading, real estate, public sector use cases; tokenized assets, title transfers, smart contracts, and verifiable certifications. |
| Challenges & considerations | Interoperability, scalability, regulatory clarity, governance, data privacy design; view as a technology investment complementing existing processes. |
| Identifying and implementing use cases | Focus on business outcomes; map data flows; run pilots with ROI, clear governance, exit/scale plans; involve IT, operations, legal, compliance, and business units. |
| What success looks like | Reduced cycle times, fewer reconciliation errors, improved data integrity, clearer audit trails; faster partner onboarding and enhanced regulatory reporting; ecosystem growth. |