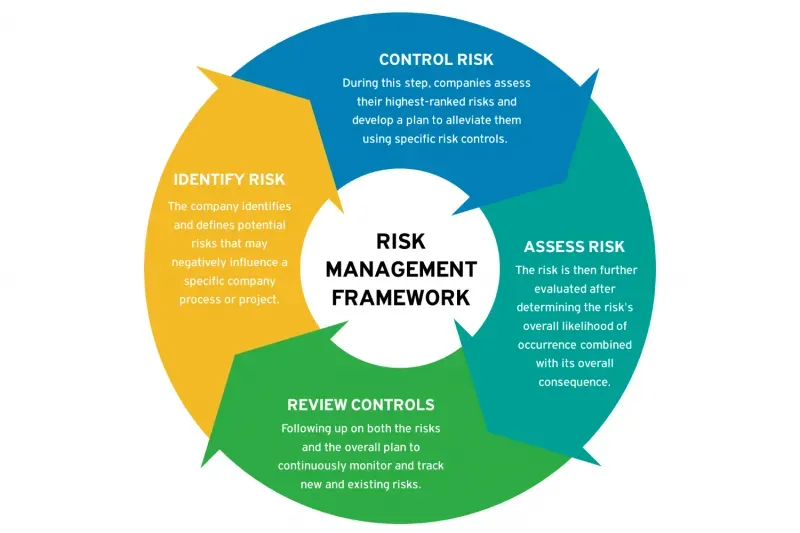
Risk management in finance is not a luxury reserved for Wall Street — it is a practical framework that helps individuals protect wealth, sustain growth, and sleep better at night. In a financial world marked by sudden market swings, credit events, inflation surprises, and regulatory changes, investors benefit from financial risk management strategies that prioritize resilience. A powerful starting point is recognizing wealth protection strategies alongside disciplined risk assessment in finance to guide diversification and capital preservation. Effective tools such as portfolio risk management, hedging and diversification, and ongoing risk monitoring help translate plans into protective outcomes. By applying disciplined analysis and clear strategies, you can build resilience into your wealth plan and move confidently toward long-term goals.
Viewed through an alternate lens, this discipline can be described as risk governance in personal finance and capital protection planning. It emphasizes identifying, measuring, and moderating exposure across markets, and it relies on scenario planning and stress testing to reveal vulnerabilities. Semantically related signals—volatility management, loss mitigation, and resilient wealth strategies—help guide thoughtful decisions even when markets wobble. In this frame, the focus shifts from chasing returns to sustaining wealth through robust controls, disciplined budgeting, and regular governance.
Risk Management in Finance: Practical Strategies for Wealth Protection
Risk management in finance is not a luxury; for individuals, it is a practical framework to safeguard capital and sustain growth. By adopting financial risk management strategies, you move from reactive responses to proactive planning, aligning risk controls with your long-term goals. Wealth protection strategies are not about avoiding risk entirely, but about shaping exposure so that losses are manageable and the path to opportunity remains intact. A disciplined approach begins with risk assessment in finance: identifying what could go wrong—from market swings to liquidity squeezes—and translating that insight into measurable thresholds, guardrails, and contingency plans. When you tie risk controls to clear objectives, you improve resilience during downturns and preserve capital for opportunities when conditions improve.
In practice, portfolio risk management becomes a daily discipline rather than a once-a-year exercise. Diversification across asset classes, geographies, and strategies reduces correlation risks, while hedging and diversification are used to cap downside without smothering upside. The toolkit of risk budgeting, liquidity planning, and regular governance helps you allocate risk intelligently rather than simply chasing returns. Through simple metrics and scenario testing, you can quantify potential losses, set limits on exposure, and adjust your plan as life evolves. The aim is a balanced, transparent framework that supports steady wealth growth even when markets are volatile.
Hedging, Diversification, and Risk Assessment in Finance: A Portfolio Risk Management Framework
Hedging and diversification sit at the core of resilient investing. By combining hedging techniques with broad diversification and a formal risk assessment in finance, you can dampen volatility without sacrificing growth. This approach aligns with financial risk management strategies and wealth protection strategies by setting guardrails around exposure, ensuring you never rely on a single bet. The focus is on understanding how different assets respond to shocks, and how hedges can offset losses when a market adverse event occurs. A portfolio that marries hedging with diversification tends to have more predictable downside and steadier compounding over time.
Portfolio risk management is dynamic and ongoing. It relies on measurable risk budgets, regular rebalancing, and explicit hedging as conditions change. Scenario analysis and stress testing reveal how withdrawals, taxes, and liquidity needs could press on the portfolio, allowing pre-emptive adjustments. By embedding hedging and diversification within a governed process, you maintain growth potential while capping downside, ensuring your plan remains aligned with long-term goals regardless of the market cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective financial risk management strategies to protect wealth during market volatility?
Financial risk management strategies focus on measuring, diversifying, and hedging to protect wealth while pursuing growth. Start with clear objectives and risk tolerance, then use diversification and asset allocation across asset classes to reduce market exposure. Use hedging and insurance (options, futures) to offset losses, and include liquidity planning and risk budgeting to limit drawdowns. Regular risk assessment in finance—via scenario analysis and stress tests—helps adjust exposures as conditions change. The goal is to manage risk, not eliminate it, to support long-term goals.
How do hedging and diversification contribute to portfolio risk management to safeguard wealth?
Portfolio risk management relies on hedging and diversification combined with disciplined asset allocation to reduce downside and capture growth. Use uncorrelated assets, dynamic rebalancing, and careful position sizing to keep risk within limits. Wealth protection strategies like liquidity planning and tax-aware investing help safeguard after-tax returns and ensure funds during downturns. Regular risk assessment in finance and scenario testing keep the approach aligned with goals, risk tolerance, and changing conditions.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Purpose |
|
| Risk Landscape |
|
| Risk Toolkit |
|
| Wealth Protection & Personal Finance |
|
| Portfolio Risk Management & Asset Allocation |
|
| Practical Plan Implementation |
|
| Tools & Techniques |
|
| Common Pitfalls |
|
| Technology, Data & Governance |
|
| Simple Example |
|